
- What are molecular ions?
- How many types of molecular ions?
- How molecular ions are formed?
- Why is NH4 + not a molecular ion? Give a reason.
- Which type of molecular ions structure exists etc.?
- Which example is suitable for molecular ions or not?
Discovery
In 1794, molecules were considered a minute particles according to the French. Latin used vogue words for molecules until the late 18th century. Molecules have evolved as the knowledge of the structure of the molecule that retains their composition and Chemical properties according to the earlier definition was less precise. This concept breaks down because most rocks, salts, and metals are composed of a huge crystalline network of chemical bonded atoms or ions.
It reveals the existence of strong chemical bonding between the atoms of molecules in ionic form.
We are searching for many years on molecular ions, including helium hydride ion, the first molecular ion we discovered that was formed in the Universe by a chemical bond. We detect it in the laboratory by inserting a medium. It was first seen in a planetary nebula named NGC 7027 using the GREAT spectrometer aboard the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy.
I will make this topic very easy for beginners.
So first of all we see its overview :
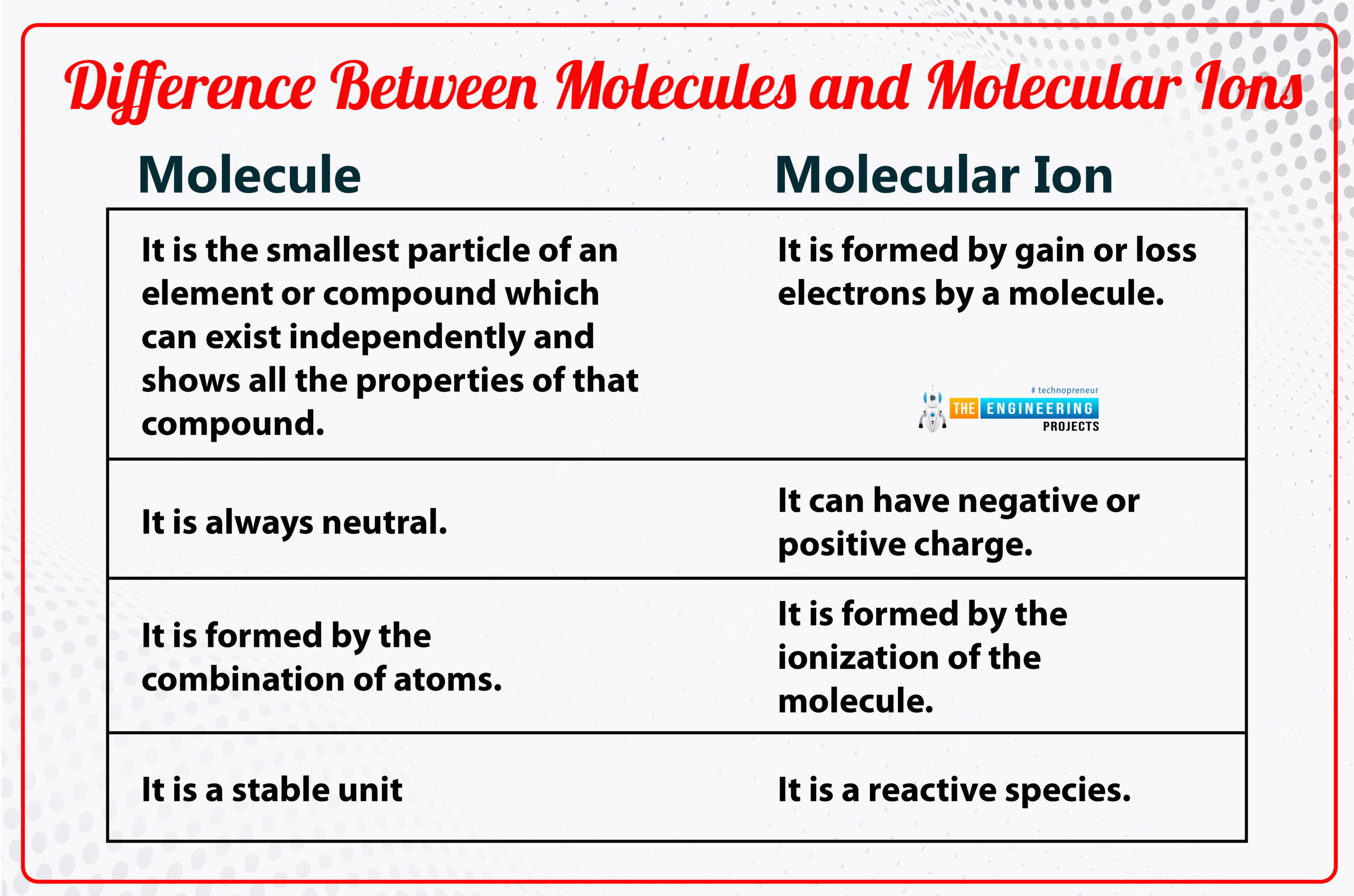
Molecular Ion:
By gaining and losing electrons of an atom, the molecular ion is formed
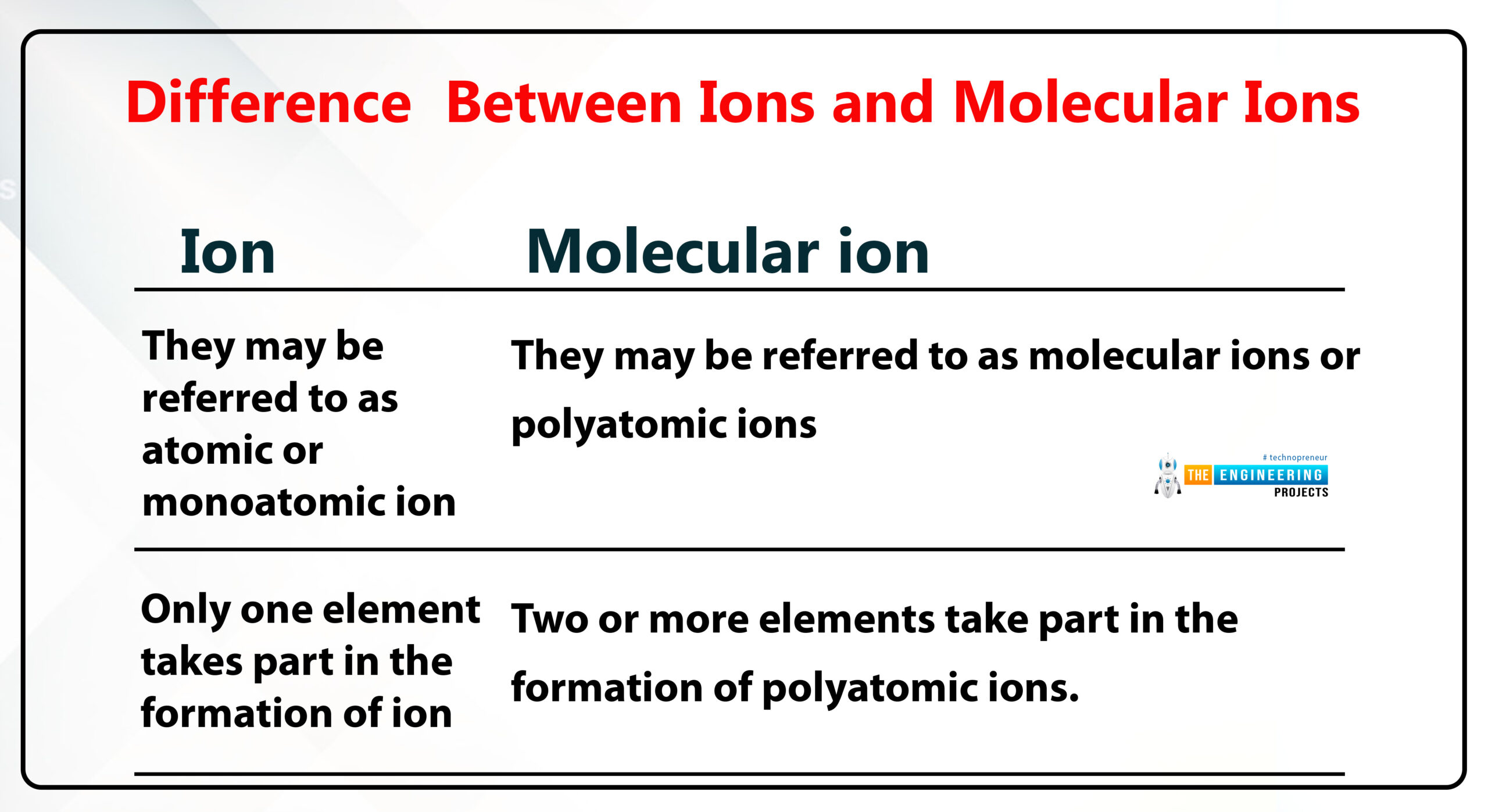
The second name of the molecular ion is also known as polyatomic ion which is formed in radical cation by a covalent bond by sharing more than one electron.
It is an example of a radical cation.
An electron is a light particle as compared to a proton.
Molecule:
it is the smallest unit of a substance and is formed by the combination of atoms.
It may contain one or more atoms.
Some examples of molecules are
- H2O (water)
- N2 (nitrogen)
- O3 (ozone)
- CaO (calcium oxide)
Difference between molecules and molecular ions:
Ion:
ion is formed by the gaining and losing of electrons of an atom.
For Example :
To understand this topic we see the example of sodium chloride NaCl.
Na+, Cl-
Difference between ions and molecular ions
Molecular compounds
- When an atom of two or more elements share electrons a molecular compound is formed
- It is also known as covalent compounds.
- In molecular compounds, the ambivalent bond is formed when atoms shared their electron pair.
Molecule ___gain/lose electron _______ molecular ion
- Types of Molecular ion:
There are two types of molecular ions:
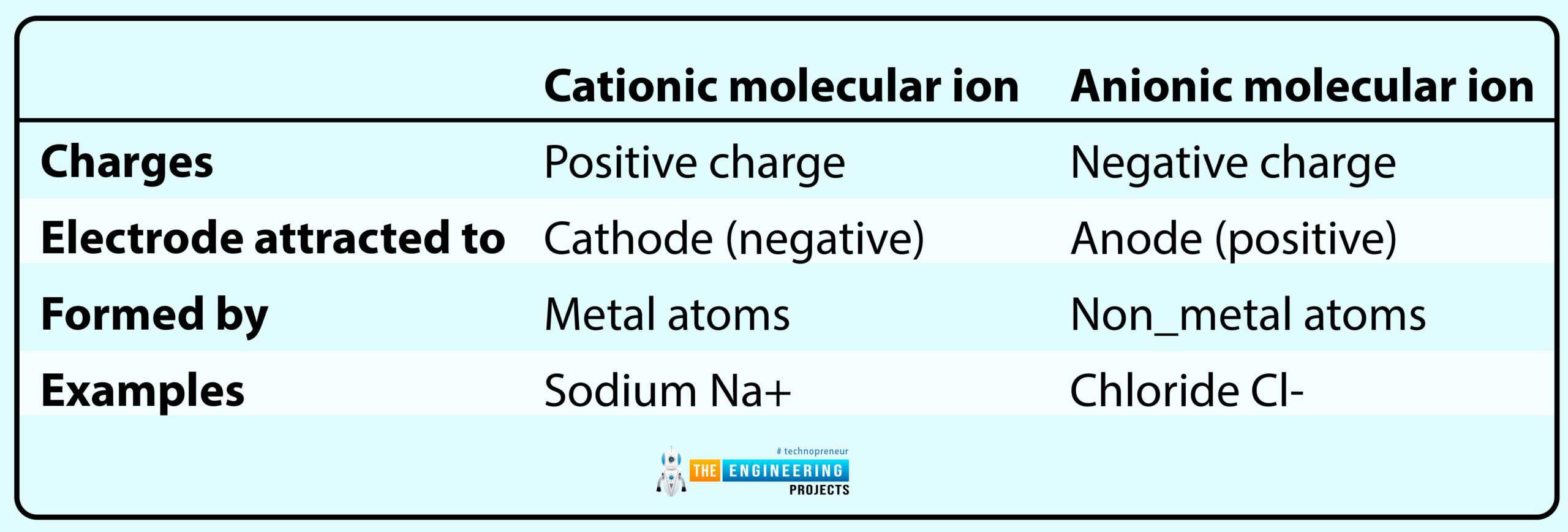
- Cationic molecular ion
They have charged positive ions because they lost the electron from the molecules.
For Example :
CH4+
- Anionic molecular ion
They have charged negative ions because they absorb the electron from the molecules.
For Example :
O2-I
The main differences between cationic and anionic molecular ions are categorized in the following table:
NOTE:
Cationic molecular ions are abundant in nature as compared to the Anionic molecular ions.
Rules of writing:
- In the naming of molecular ions, caution is written first and the anion is written in second no.
- Ion is written in the bracket if the formula unit contains two or more of the same polyAtomic ion with subscript written outside the bracket.
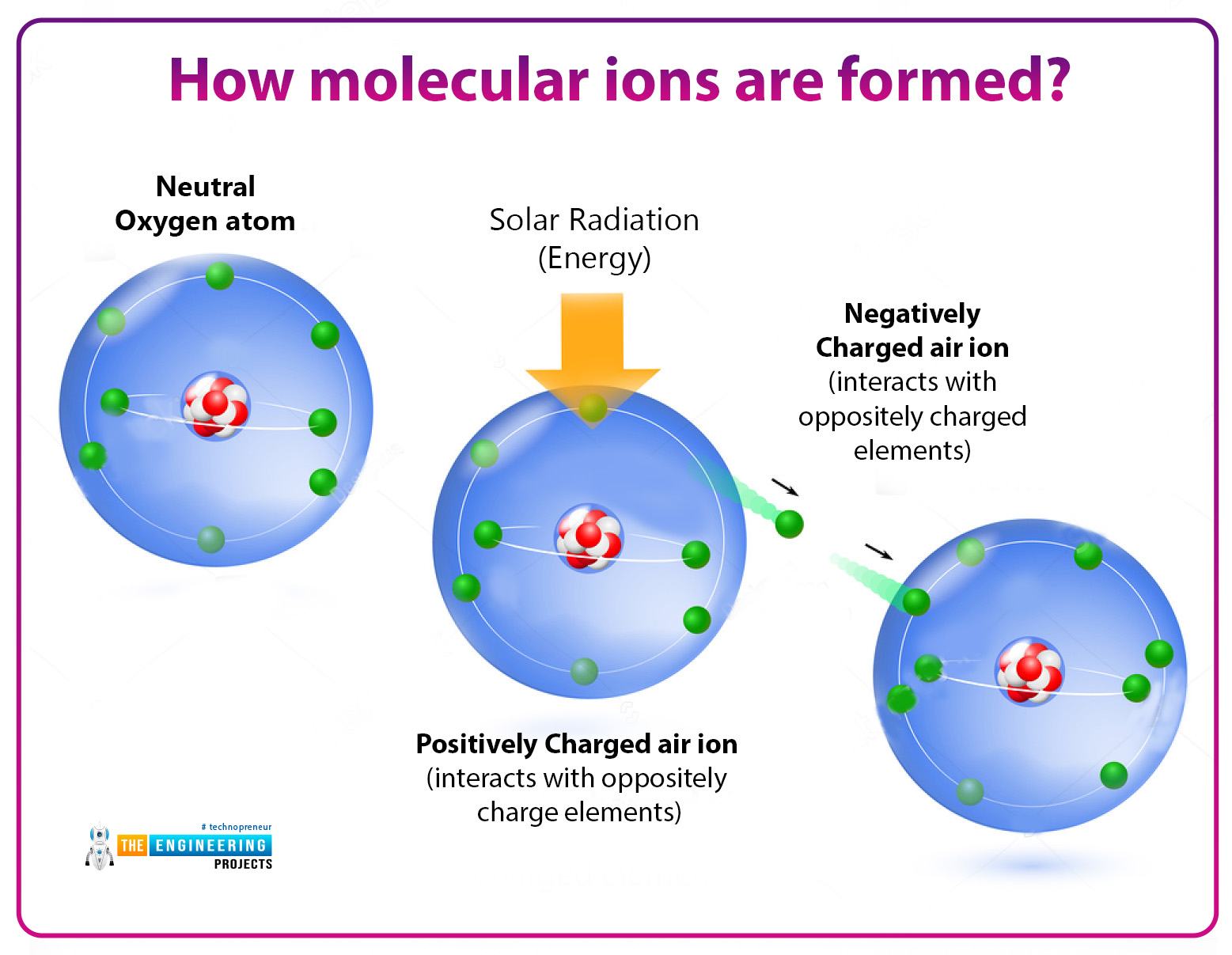
How molecular ions are formed?
These cations and anions are formed by the bombardment of high-energy particles such as electron beams in the form of alpha particles or X_rays. These rays or radiation knocked out the electron from gas molecules resulting in the formation of Cationic molecular ions.
Simply we can say that it is formed by the ionization of the molecules.
For Example :
N2 + 1e– ___x_rays/alpha rays______N2-1 (molecular anion)
CO ___alpha/x_rays_____ CO+ + 1e-1 (molecular cation)
Explanation :
In the first example, we deal with a nitrogen molecule in which it gains one electron in the presence of a beam of X_rays or alpha rays radiation and becomes a molecular anion. Molecular anions are less abundant in nature. To understand this topic we take the example of bags and clothes. If you put the clothes in a bag, if the bag is almost full then it is difficult to put more clothes in bags. This is the same logic apply to molecular anions.
That’s why it is less abundant.
In the second example, we release electrons from CO, in the presence of X_rays then we format molecular cation because it is easier to remove electrons from more than one.
It is very abundant in nature.
- Features of formation of molecular ion:
There are important features that tell us how an electron is removed from bond pair:
- Electrons are easily removed from non_bonded pairs as compared to bonded pairs.
- Because bonded pairs are at lower energy levels and most localized as compared to non_bonded pairs.
- It is most difficult to lose electrons from bonded pairs.
The most important thing here arises is that,
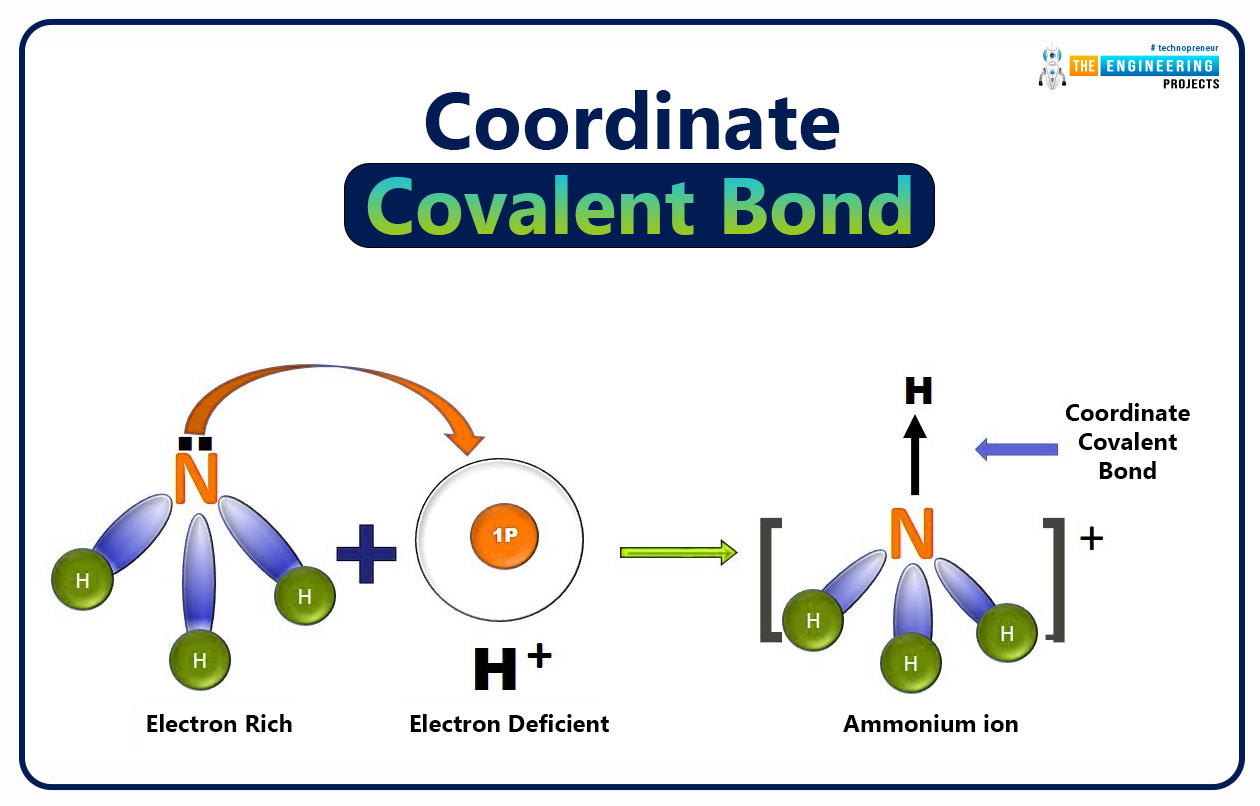
Is Ammonium ion (NH4+ ) a molecular ion?
The ammonium ion is not a molecular ion due to its formation through the coordinate covalent bond between ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen ion (H+).
Because nitrogen of ammonia has electron lone_pair it can donate electrons to hydrogen ions resulting in the formation of ammonium ion by dative bond or co_ordinate covalent bond.
Hence, ammonium ion (NH4+) is not formed by the gain or loss of electrons. Therefore it is not a molecular ion.
NH4+ is a poly-atomic ion.
Is ozone a molecule?
Ozone is also a molecule that is bound by three atoms of oxygen. Which is symbolically represented by O3.
Its layer protects our environment or atmosphere from harmful ultraviolet rays which are emitted by the sun.
Identification of molecular ions:
If molecules have any species of the charge they will be molecular ions if we remove the charge from the molecule then it is simply a molecule, not a molecular ion.
CH4+ (molecular ion)
CH4 (Molecule not a molecular ion)
What is the molecular mass?
The total atomic mass of all elements present in a molecule is equal to that of a particular substance known as molecular mass.
How can we measure the molecular mass?
We can measure the molecular mass of the molecule by using the following steps which are given below:
- First of all, we define the formula of a molecule.
- We find out how many atoms are present in a molecule.
- Then we multiply the atomic weight of an element by the number of atoms.
- Similarly, the same process applies to all elements in a molecule.
Example:
See the example of calcium oxide (CaO).
Sum up all the values we obtain,
CaO = 1*40(atomic mass of calcium) + 1*16(atomic mass of oxygen)
= 56 g_mol-1
What is the formula mass?
The sum of the atomic mass of all the elements present in a formula unit of a substance is called formula mass.
For Example :
The formula mass of NaCl is 58.5 atomic mass.
Which type of force exists in molecular ions formation?
Intermolecular forces:
Intermolecular forces are electrostatic attractive forces between permanently or temporarily charged chemical species. They include
- Van Der Waals forces (attractive forces)
- Dipole-dipole forces
- Ion_ion forces
- Hydrogen bonding
Van Der Waals forces:
These forces are responsible for the formation of molecular ions.
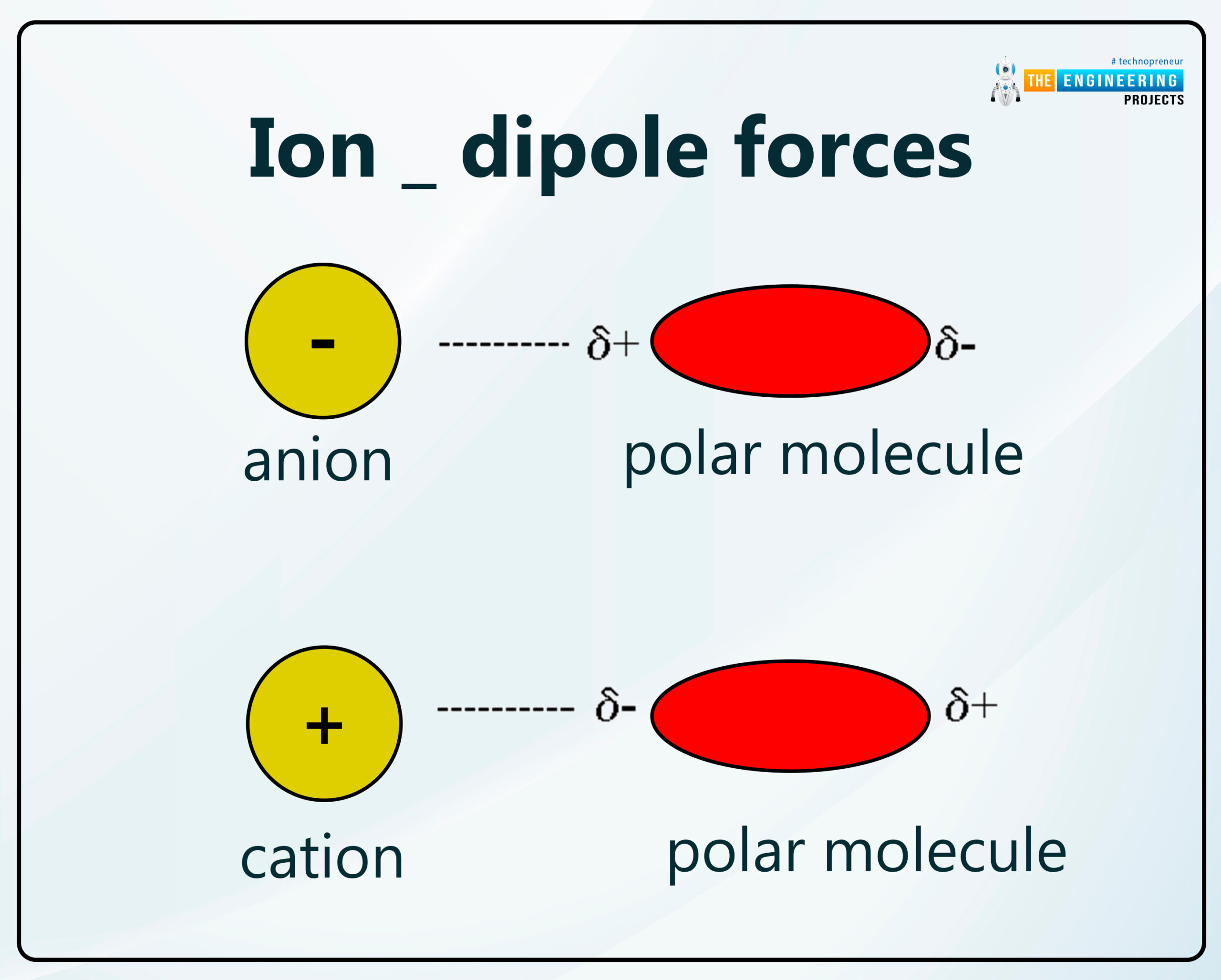
Ion _ dipole forces:
Dipole-dipole or an ion-dipole force is an attractive force that resultantly comes from the electrostatic attraction between an ion and a neutral molecule that has a dipole.
A positive molecular ion (cation) attracts the partially negative end of a neutral polar molecule.
A negative molecular ion (anion) attracts the partially positive end of a neutral polar molecule.
Ion_ion forces:
Ion_ion forces are also known as ionic bonding. It is easy to understand this force is present between two oppositely charged ions. This force is not considered an intermolecular force but this force is helping us to understand this bonding.
A suitable example for this case is table salt, NaCl.
Hydrogen bonding:
Hydrogen bonding also plays a vital role in the formation of molecular ions. This force is stronger than all types of forces. Its best example is water in the formation of molecular ions.
How do you determine the molecular ions?
how to find the relative formula mass by using a molecular ion?
In mass spectroscopy, an electron is released from the molecule; then as a result we obtain a radical cation called the molecular ion (symbols: M•+, M+).
The molecules which removed the electrons resultantly gain molecular ions currently obtained the highest energy electrons
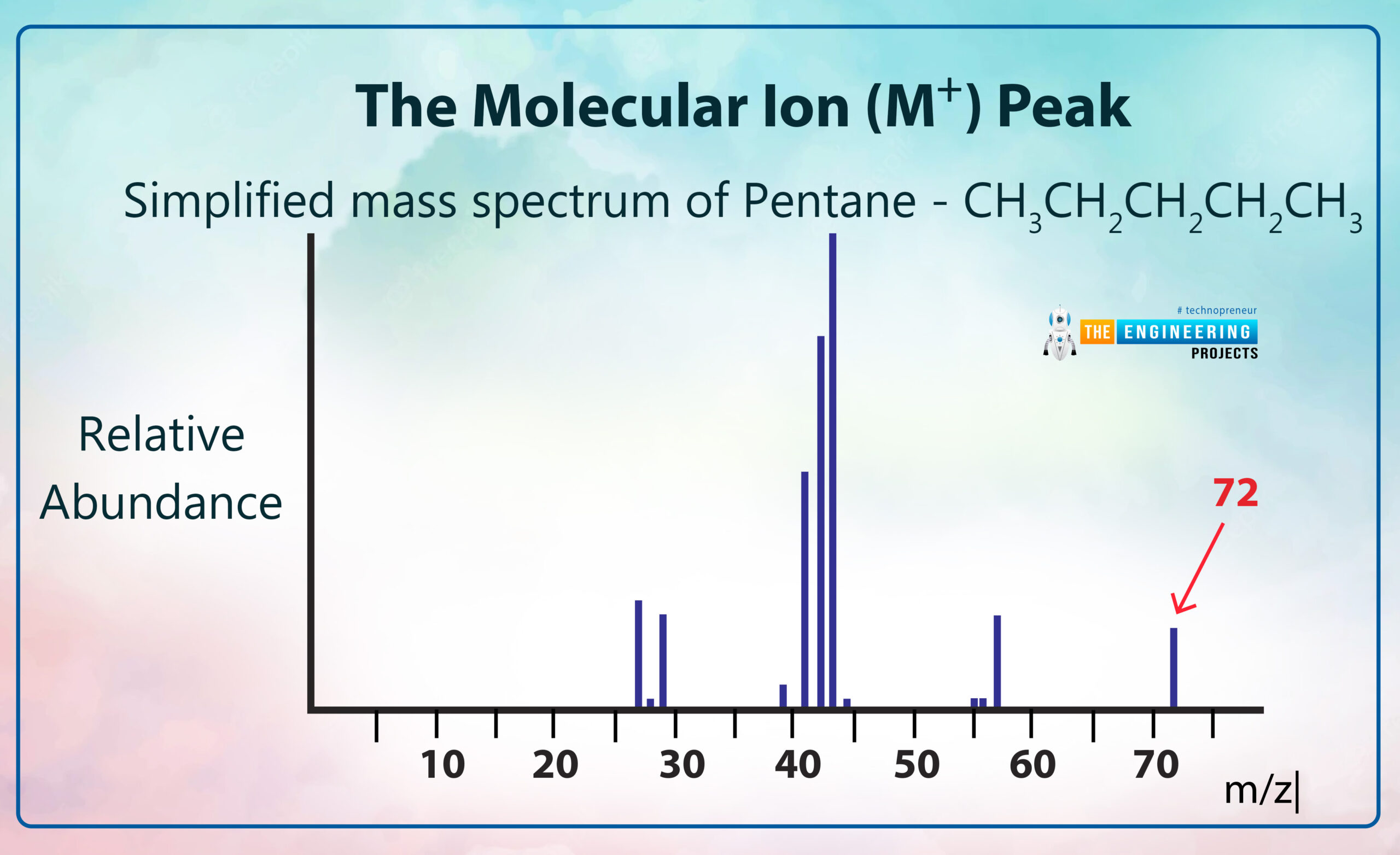
The Molecular Ion (M⁺) Peak:
We describe the molecular ion peak by using a graph:
In this peak, we can describe the relative formula mass (relative molecular mass) of an organic compound from its mass spectrum. It also gives us high-resolution mass spectra that can be able to find out the molecular formula for a compound.
In the mass spectrum, the ion which has the greatest m/z value is treated like a molecular ion. Some ionic compounds have mass spectra that don’t contain a molecular ion peak because all the molecular ions break into fragments.
By the end of this article, you will be able to find out
Important Facts:
By using molecular ions we can determine the following facts:
- Determination of the molecular mass.
- Structure of a compound
- Kinds of bond
- Kinds of atoms
The most important question is what molecular ions how they are formed.
Significance/Applications:
Molecular ions obtained from the natural products on decomposition give information about the structure of the molecule.
I Hope, I cover all aspects of the molecular ions. It is the last topic of our first tutorial. If you want these trusting topics simply, give me good feedback for better results. If you have any questions, put them in the comment section. I will reply to you as soon as possible. Our next tutorial series is coming soon. Our platform tries to give the best and in trusting topics that clear your all concept. Thanks.
JLCPCB – Prototype 10 PCBs for $2 (For Any Color)
China’s Largest PCB Prototype Enterprise, 600,000+ Customers & 10,000+ Online Orders Daily
How to Get PCB Cash Coupon from JLCPCB: https://bit.ly/2GMCH9w
The post Introduction to Molecular Ions appeared first on The Engineering Projects.

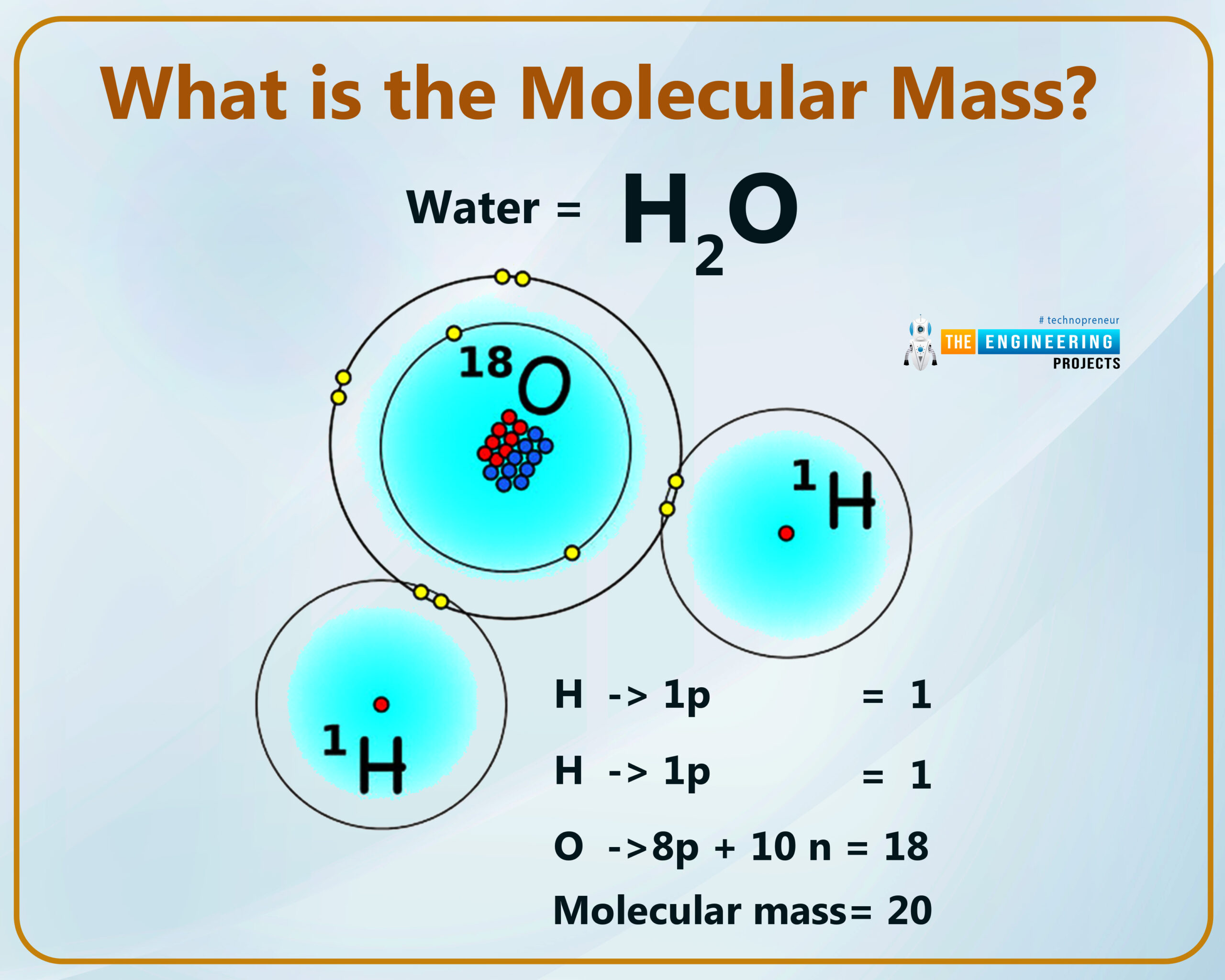
No comments:
Post a Comment