 Hello, readers!
Hello, readers!
In today’s lesson, we’ll go over another characteristic of the esp32 module that helps it stand out from the competition: BLE or Bluetooth Low Energy. It’s our 3rd tutorial in the ESP32 programming series. In the first tutorial, we have seen a detailed Introduction ESP32, while in the second tutorial, we have created a web server using ESP32.
We will first look at what BLE is and what it can be used for in this lesson, and then we will look at some examples utilizing the ESP32 and the Arduino IDE.
What is BLE?
- There have been numerous adjustments and upgrades to Bluetooth’s characteristics since its inception, where Bluetooth 4.0 or BLE or Bluetooth smart is the most influential.
- BEL or Bluetooth Smart is also known as Wibree. The Wibree protocol was designed by Nokia in 2006 and was later included in Bluetooth 4.0 as Bluetooth Low Energy in December 2009.
- Bluetooth Low Energy is a somewhat different protocol from regular Bluetooth, which is used in phones, headphones, TV etc. Rather than continuously streaming data, BLE “servers” can “notify” clients to send them pieces of data on a regular basis(which makes it preferable over traditional Bluetooth). As a result, BLE is better suited to low-power IoT applications that don’t require significant volumes of data.
- Both the server and clients now utilize a “service UUID”, which describes the overarching service, to determine which server and client to connect to. There are various “characteristics” that can be found inside these services.
- Bluetooth Low Energy was developed and promoted by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) for use in healthcare, beacons, fitness and home entertainment etc. It does not work with standard Bluetooth and does not have any compatibility, although it can coexist with BR/EDR and LE.
- The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) recognizes a number of industries for low-energy technology, including smart homes, health, sport, and fitness.
Difference b/w traditional Bluetooth and BLE
- It’s crucial to discuss power usage while discussing the differences between Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy. Bluetooth was created with the intention of allowing data to be streamed indefinitely. That implies you can send and receive a large amount of data over a short distance.
- Whereas, Bluetooth Low Energy is intended to transfer data only when the client is available to receive the data from the server; otherwise, the BLE device will go into low energy or sleep mode. Thus, use significantly less power and cost while retaining a similar communication range.
- Bluetooth Low Energy uses the same 2.4 GHz radio frequencies as traditional Bluetooth, but a different FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) technique.
- Classic Bluetooth uses Scatter-net topology whereas BLE uses Star topology.
Although Bluetooth Low Energy differs from the previous Bluetooth Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate protocol, both can be supported by the same device: the Bluetooth 4.0 specification allows devices to implement any or both of the LE and BR/EDR systems.
Because both, Bluetooth Low Energy and traditional Bluetooth use the same 2.4 GHz radio frequencies, allowing dual-mode devices to use a single radio antenna.
How does BLE work?
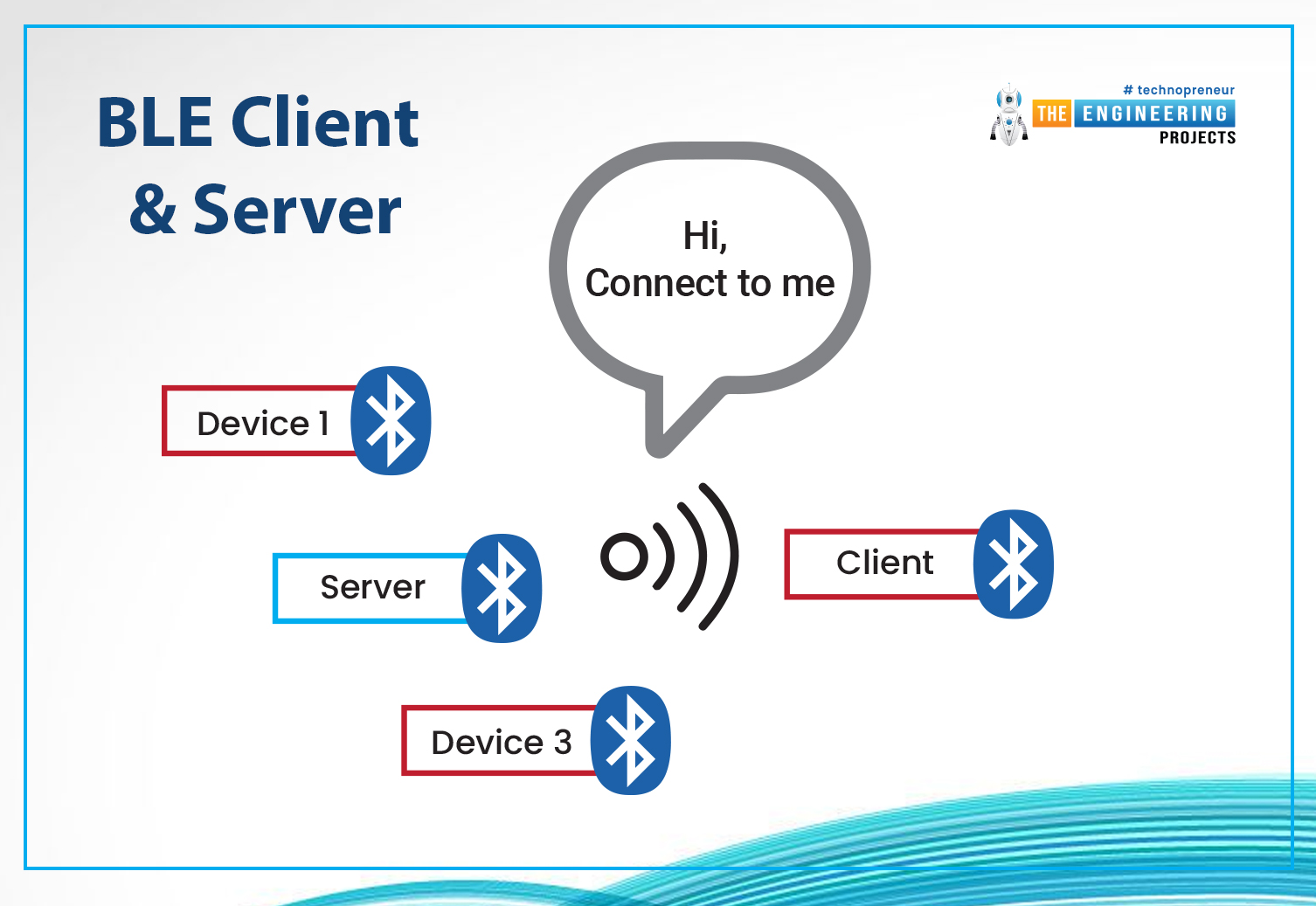
BLE Client & Server
- Any BLE device can function as both a server and a client.
- Server ESP32 will announce its presence to nearby clients so that clients can establish a connection with the BLE server for communication.
- Broadcast mode and mesh networks both are also supported by BLE.
- In broadcast mode, only the BLE server transmits data to all the connected clients.
- In mesh mode, all the devices are connected to each other. Therefore, all devices can communicate with all other available devices.
GATT
- GATT is an acronym for Generic Attributes.
It defines a data structure that is visible to all BLE devices linked to it. GATT defines how BLE devices can communicate with each other. Understanding this structure is crucial since it will make it easier to learn how to use the BLE.
The GATT protocol includes a set of commands that allow the client to learn more about the server.
- Read through all of the descriptors for a specific characteristic.
- Find out everything there is to know about a specific service.
- Find qualities that match a UUID.
- Find UUIDs for all major services.
- Find a service using a UUID.
- For a particular principal service, locate subsidiary services.
BLE Service
- A profile, which is made up of multiple services, is at the top of the structure. Typically, a BLE-supported device will have multiple services.
- The SIG has preset services for a variety of data kinds, such as battery level, weight, blood pressure, heart rate, and so on.
- Every service has at least a single feature and can also refer to different services. A service is nothing more than a collection of data, such as data from a temperature sensor.
BLE Characteristics
The characteristic attribute is always held by a particular service, and it is where the hierarchy’s real data is stored.
The characteristic has two attributes:
- Characteristic value
- the characteristic declaration which contains the metadata
It essentially consists of the operations that can be used with the characters like Indicate, read, write, notify, broadcast etc.
UUID or Universally Unique Identifier
- In a Generic Attribute (GATT) profile, the UUID is a universally unique 128-bit or 16-byte integer that is used to identify profiles, services, and data kinds.
Note:
- In the code description we will provide a link where you can generate a new UUID.
BLE network topology
BLE uses Star and mesh topology for communication.
A Broadcast Type or a Connection Type communication between two BLE devices is possible. The ‘broadcaster’ BLE Device sends data to any ‘observer’ BLE Device in broadcasting. It’s a data transfer that only goes one way.
A ‘Connection’ between the BLE Devices is required for two-way communication. A Central (Master) BLE Device continuously checks for advertising data packets sent by a Peripheral (Slave) BLE Device.
BLE Applications
- BLE is ideal for applications that need to exchange modest amounts of data on a regular basis.
- BLE is used extensively in healthcare, fitness, tracking, beacons, security, and home automation etc.
- Bluetooth Low Energy is natively supported by mobile operating systems such as iOS, Android, Windows Phone, as well as macOS, Linux, Windows 8 & 10.
ESP32 BLE
- You can use ESP32 BLE either as a BLE server or a client.
- Examples are available in the ESP32 BLE library(Arduino IDE) which you can use to implement BLE services.
Note:
- The Arduino IDE must have the ESP32 board manager file and libraries installed. If you haven’t previously, prepare your Arduino IDE to operate with the ESP32 then do read our previous tutorial i.e. Introduction to ESP32 Programming Series.
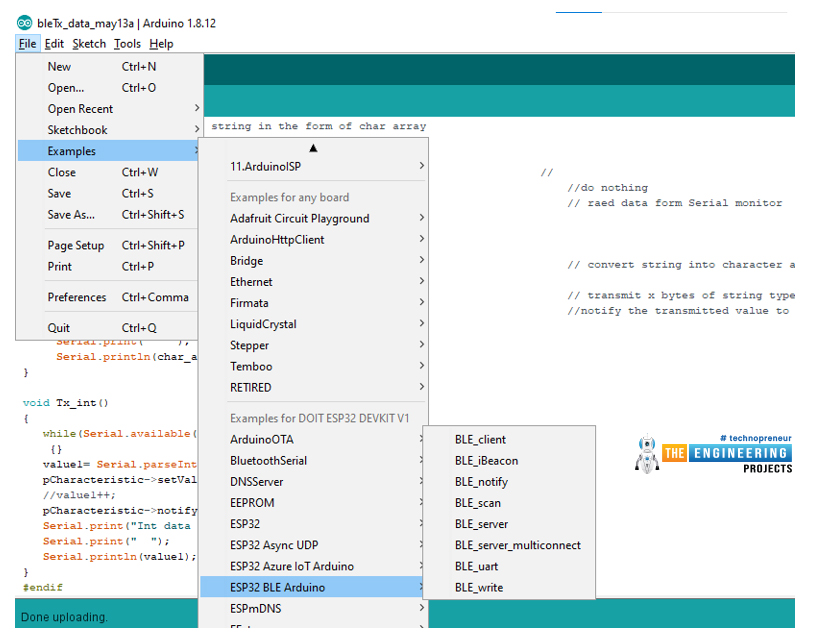
BLE Server Code Description
- For coding, we are using Arduino IDE’s inbuilt example and will make required changes in that code only.
- I will also explain the code in detail for beginners to understand.
In this code ESP32, BLE will be used as a server.
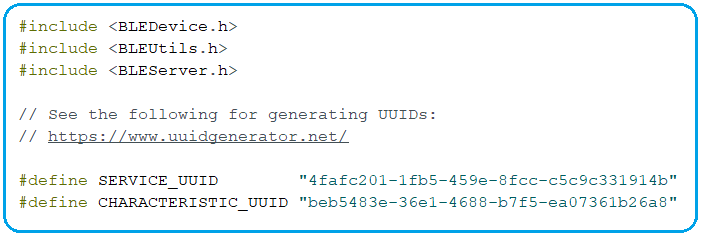
- Import the necessary/required libraries for the BLE application.
- Define a UUID for the Service and Characteristic.
- To generate UUIDs, go to the following link:
https://ift.tt/1MfVeDK
- You can either use the default UUIDs if you wish to or go to the above link to generate random UUIDs as per your services and attributes.
- Call back or acknowledge the server whether the client is connected or not
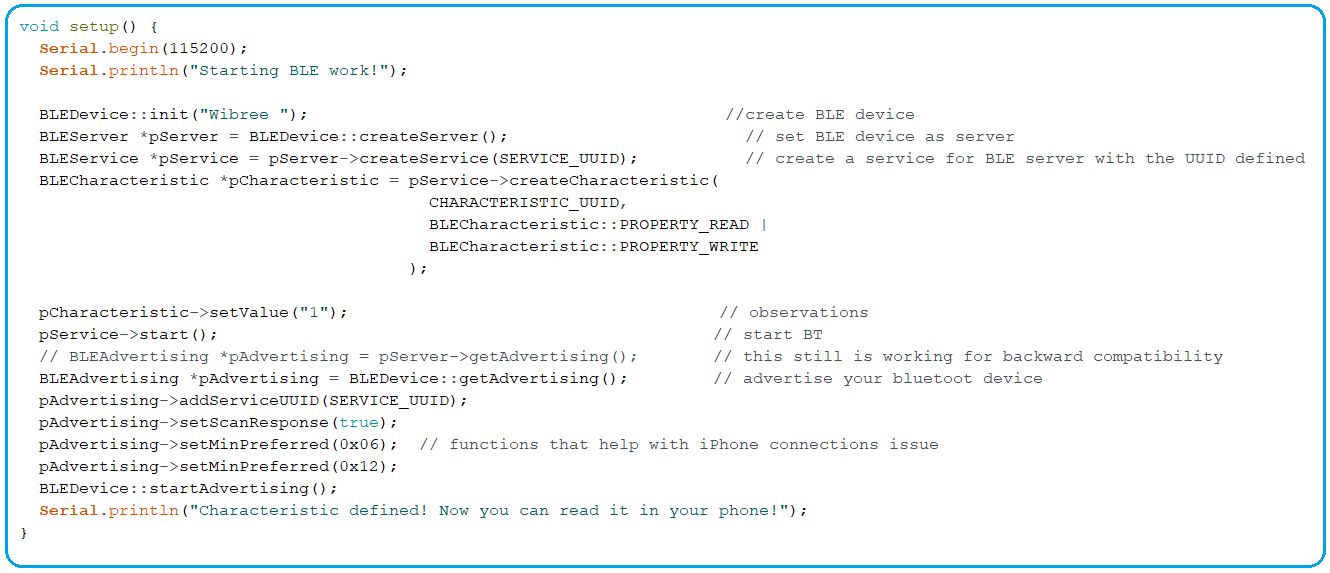
Arduino Setup() Function
- Serial Communication at a baud rate of 115200.
- Create a name for your BLE device for identification, we named it Wibree.
- Set the BLE device as a server.
- Create a service for the BLE server with the UUID defined earlier.
- The characteristic for that service is then set. As you can see, you’re still using the UUID you created previously, and you’ll need to supply the properties of the characters as arguments. It’s read and write in this scenario.
- You can also add other services like battery, indicate, notify etc.
- The setValue() method can be used to set the value of a characteristic.
- The above value can be changed to whatever you like. This could be a sensor reading.
- Finally, activate the service and advertising so that other BLE devices can scan and locate this BLE device.
Arduino Loop() Function
- Here we can check if the device is connected with the client or not
- If connected then do some tasks like transmitting data or receiving input from the client.
Data Size Per Packet
20 bytes per packet.
Unfortunately, BLE isn’t built to handle large amounts of data. The maximum data size per packet in the BLE specification is 20 bytes, so if you wish to communicate more, you’ll have to divide it up into many packets. Fortunately, this isn’t a tough task. Simply put, use a delimiter like “!” or “*” or something unique at the end of your whole message to signal the app that the message is done and to start listening for future communications. If you want to send and + > 20 bytes cumulatively, for example, you can send and then proceed with the next message if needed.
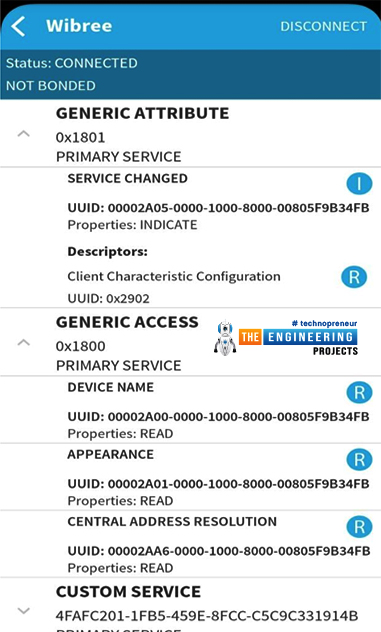
Testing ESP32 BLE Server
After creating a BLE server using ESP32, we can use a BLE application available on the Play store for testing purposes.
Demonstration with BLE scanner app:
- Go to play store
- Search for BLE scanner and download the app
- After installing the app turn on the Bluetooth.
- Open the app and search for nearby devices.
- Now connect to ESP32 BLE by clicking on the ESP32 device.
- In our case, we named the device ‘Wibree’.
- Now you can use the various services provided by BLE like writing and reading data packets, checking battery levels etc. and a lot more.
This concludes the tutorial. I hope you find it helpful.
JLCPCB – Prototype 10 PCBs for $2 (For Any Color)
China’s Largest PCB Prototype Enterprise, 600,000+ Customers & 10,000+ Online Orders Daily
How to Get PCB Cash Coupon from JLCPCB: https://bit.ly/2GMCH9w
The post ESP32 BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) appeared first on The Engineering Projects.




No comments:
Post a Comment