 Hello Everyone! Hope you’re well today. Thank you for viewing this read. In this post today, I’ll be discussing the Introduction to BC640. BC640 is a bipolar junction transistor that belongs to the PNP transistor family. It is composed of silicon material and comes in a TO-92 package. It is used to drive load under 500mA. In this post, you’ll get to know everything related to BC640 covering pinout, working, alternatives, applications, and physical dimensions.
Hello Everyone! Hope you’re well today. Thank you for viewing this read. In this post today, I’ll be discussing the Introduction to BC640. BC640 is a bipolar junction transistor that belongs to the PNP transistor family. It is composed of silicon material and comes in a TO-92 package. It is used to drive load under 500mA. In this post, you’ll get to know everything related to BC640 covering pinout, working, alternatives, applications, and physical dimensions.
Keep reading.
Introduction to BC640
- BC640 is a PNP bipolar junction transistor mainly used for amplification and switching purpose.
- It comes with three pins called the emitter, base, and collector.
- The base is the main terminal responsible for the entire transistor reaction. The small current change at the base terminal is used to control large current across remaining terminals. The reason, it’s also called current controlled device in contrast to FET (field-effect transistors) which is a voltage-controlled device.
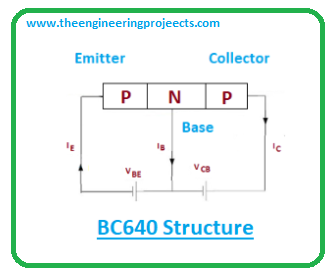
- BC640 carries three layers where one n-doped layer is placed between two p-doped layers.
- As this is a PNP transistor, here current flows from emitter to collector as opposed to NPN transistor where current flows from collector to emitter.
- Both holes and electrons play a critical role in conductivity. In the case of PNP transistors, holes are the majority carriers and electrons are major charge carriers in NPN transistors.
- It is important to note that NPN transistors are preferred over PNP transistors because the movement of electron is better and faster than the movement of holes. In some electronic projects, both PNP and its complementary NPN are combined and incorporated into a single circuit.
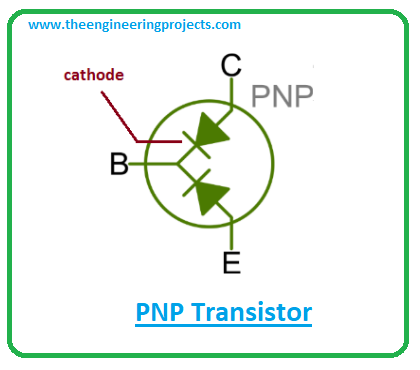
- When two diodes are joined together from the cathode side, they produce PNP transistors. Here N-layer represents the base terminal while remaining layers represents emitter and collector respectively.
- In PNP transistor there is no current at the base side when the transistor is turned ON, while in NPN transistor electrons start flowing through the base terminal when the bias voltage is applied.
BC640 Datasheet
- It’s always better to sift through the datasheet and get a hold of the main features of the component.
- Download BC640 datasheet by clicking the button given below:
BC640 Pinout
BC640 carries three pins named:
1: Emitter
2: Base
3: Collector
The following figure shows the pinout of BC640.
- All these pins are used for the external connection with the electronic circuits, and they all are different in terms of their functions and doping concentrations.
- The doping concentration in the emitter terminal is higher than both base and collector terminals.
BC640 Working Principle
- Both PNP and NPN transistors almost work similarly with some exceptions.
- The voltage polarities and current directions in PNP transistors appear opposite compared to NPN transistors.
- The base is still considered the main area responsible for the overall transistor action.
- As holes are majority carriers in this PNP transistor, now holes are emitted from the emitter terminal (electrons are emitted from the emitter in case of NPN transistor) which are then collected by the collector.
- It is important to note that when there is no current present at the base terminal, PNP transistor is turned ON and when current flows through the base it is considered turned OFF.
BC640 Power Ratings
The following image shows the absolute maximum ratings of BC640.
| Absolute Maximum Ratings BC639 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Rating | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| 1 | Collector-Emitter Voltage | Vce | 80 | V |
| 2 | Collector-Base Voltage | Vcb | 80 | V |
| 3 | Emitter-Base Voltage | Veb | 5 | V |
| 4 | Collector Current | Ic | 500 | mA |
| 5 | Total Device Dissipation | Pd | 625 | mW |
| 6 | Transition Frequency | ft | 50 | MHz |
| 7 | Storage Temperature | Tstg | -55 to 150 | C |
- Both collector-emitter and collector-base voltages are 80V while the emitter-base voltage is only 5V which means the only 5V is required to trigger the transistor reaction.
- Device dissipation is 625mW which implies the amount of heat it produces as a byproduct due to its primary action.
- Collector current is 500mA which projects the value of load it can drive. The transition frequency is 50MHz which is a measure of the high-frequency operating characteristics of a transistor.
- These are the stress ratings. Make sure these ratings don’t surpass the absolute maximum ratings, else they will damage the component, thus the entire project.
- Moreover, extended exposure to stresses above recommended absolute maximum ratings can influence the device reliability.
Difference between PNP and NPN transistors
- Current direction is the major difference in both NPN and PNP transistors.
- Recall, current flows from emitter to collector in PNP transistor when a negative voltage is applied to the base terminal and current flows from collector to emitter in NPN transistor when a positive voltage is applied at the base terminal.
- In both cases, the base terminal is responsible for the electron reaction.
- In NPN transistor, the transistor turns on when current flows through the base terminal, and in case of PNP transistor, the device turns on when there is no current at the base terminal.
- Both transistors are the primary components used in modern electronic projects.
- It is important to note that both NPN and PNP transistors are interchangeable and are made up of two back to back diodes where one is forward biased and the other is reverse biased.
- The main difference stands in the polarities of the applied voltage at the base terminal and current direction as mentioned above.
- In conclusion, both PNP and NPN are interchangeable and work perfectly well if we change the polarity of the applied voltage.
BC640 Alternatives
Following are BC640 alternatives:
- BC618
- BC635
- BC636
- BC637
Better check the pinout of the alternatives before embedding them into your projects, as it’s likely they might carry different pinout than BC640.
The complementary NPN transistor to the BC640 is BC639.
BC640 Applications
The following are some applications of the BC640.
- It is used to source current, i.e. current flows out of the collector.
- Used for switching and amplification purpose.
- Used in electronic motors to control current.
- Employed in the push button.
- Used in robotics and instrumentation.
- Finds applications in Darlington pair circuits.
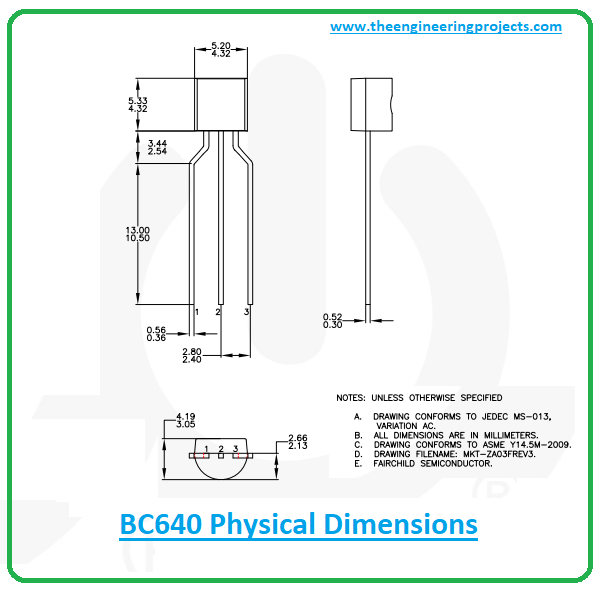
BC640 Physical dimensions
The following figure shows the physical dimensions of the BC640.
That’s all for today. I hope you’ve got an insight into the Introduction to BC640. If you have any question, you can approach me in the comment section below, I’d love to help you the best way I can. You’re most welcome to share your feedback and suggestions, they help us provide quality work. Thank you for reading this post.
JLCPCB – Prototype 10 PCBs for $2 (For Any Color)
China’s Largest PCB Prototype Enterprise, 600,000+ Customers & 10,000+ Online Orders Daily
How to Get PCB Cash Coupon from JLCPCB: https://bit.ly/2GMCH9w
The post Introduction to BC640 appeared first on The Engineering Projects.



No comments:
Post a Comment